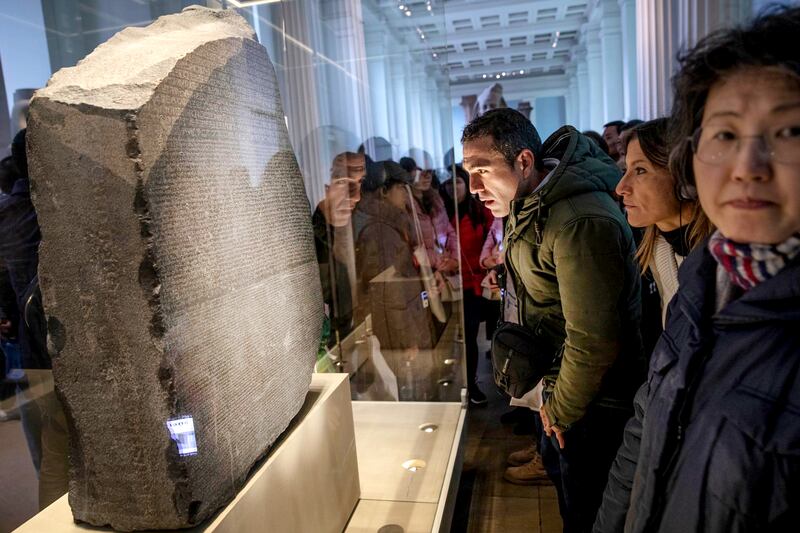
A renowned Egyptian archaeologist is about to launch a new push to bring the Rosetta Stone back to its homeland from the British Museum, tapping into a changing mood in Europe about the rightful home of colonial-era trophies.
Dr Zahi Hawass, a larger-than-life Egyptologist and former antiquities minister who once escorted Barack Obama around the pyramids, believes people in Europe “are really awakening” to his cause.
The 2,200-year-old Stone that unlocked the mystery of Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics is one of three prize treasures he wants back from European museums, along with a bust of Queen Nefertiti in Berlin and a sculpted Zodiac ceiling at the Louvre in Paris.
Dr Hawass, who turned 75 in May and is known for his Indiana Jones explorer's hat ("mine is the real Egyptologist's hat," he once said), has been banging the drum for years for the return of the three items.
But he plans to relaunch his effort with a petition signed by a group of Egyptian intellectuals, which he will start sending to the European museums in October.
“I believe those three items are unique and their home should be in Egypt. We collected all the evidence that proves that these three items are stolen from Egypt,” he told The National.
“The Rosetta Stone is the icon of Egyptian identity. The British Museum has no right to show this artefact to the public.”
The museum, for its part, said there has never been a formal request to return the ancient tablet to Egypt, and one line of thinking is that not everyone in the Egyptology world shares Dr Hawass’s fixation with the Rosetta Stone.
But there are signs that the tide is turning on the wider, emotionally-charged question of returning ancient artefacts. Germany recently said it was “moving into a future” where the looted Benin Bronzes would be owned by the people of Nigeria.
The British Museum pushed the door open to a compromise over the Parthenon Marbles, also known as the Elgin Marbles, by calling for a “Parthenon Partnership” involving loans of the Ancient Greek sculptures.
“There is a change in the air in this respect,” said Alexander Herman, the director of the Institute of Art and Law in Britain. “Some of the old arguments, the ones that used to hold sway for so long, are beginning to wear thin.”

Prize artefact
The Rosetta Stone has been in the British Museum since 1802, when Britain acquired it from France under a treaty signed during the Napoleonic Wars.
Napoleon’s troops had apparently stumbled upon the Stone while building a fort near the town of Rashid, or Rosetta, and realised the significance of the hieroglyphics, Ancient Greek and cursive Egyptian letters inscribed upon it.
It was the breakthrough that allowed the ancient hieroglyphics to be read and understood for the first time in centuries, making the Stone one of the British Museum’s most famous possessions.
But Dr Hawass believes it left his country illegally and has campaigned on the subject since his time as antiquities minister, when he brought thousands of artefacts back to Egypt, toured the pyramids with Barack Obama and was known for ruffling diplomatic feathers.
As head of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, which was his formal title, he informed former British Museum director Neil MacGregor as far back as 2003 that he would go into battle with the museum if it did not agree to hand back the Stone voluntarily.
His political career ended in acrimony after the fall of Hosni Mubarak in the 2011 revolution, but he was cleared of corruption charges and has maintained his quest for the Stone, Nefertiti and the Zodiac as a private citizen.
"They left Egypt completely illegally and they should come back," he said.
Dr Hawass takes encouragement from French President Emmanuel Macron’s willingness to return plundered art to his country’s former African colonies, another sign of the changing landscape.

The factors behind the shift include the increasing stability of some countries seeking the return of artefacts, said Prof Peter Stone, an expert on protecting cultural heritage at Newcastle University and an adviser to Unesco.
“One of the arguments about not returning material was that it might be stolen in the future from the host country. I think that’s now a fairly pale excuse,” he said.
Mr Herman, the author of a book on restitution, said modern technology was another factor because it raised global awareness of the items belonging to European museums and allowed people to organise campaigns to return them.
The internet age also gives researchers more access to documents about the history of an object, where it has been and how it might have been taken at some point in the past, he said.
There was the climate of colonial contrition that grew out of the global anti-racism protests in 2020, prompting calls to tear down statues and other legacies of imperialism around the world.
The Arts Council in England this month published 33 pages of guidance for museums being harangued about their collections, telling them to be sensitive and consider handing back certain items where appropriate.
Drawn up with the help of Mr Herman’s institute, the guidance suggests compromises such as arranging long-term loans for sensitive items, even if museums are not willing to give up ownership.
In other recent examples, London's Horniman Museum said it would return 72 objects to Nigeria that were looted in 1897, and the National Museum of Scotland was speaking to Canadian First Nation leaders about a disputed memorial pole.

“Every case is going to be different, these issues have to be dealt with on a case-by case basis,” said Mr Herman.
“One particular artefact may be better placed in its home country and not in a museum in the West, but you might have another artefact where once you’ve looked at all the factors involved, it’s better suited to a museum context, it’s better looked after, it’s better understood in that way.”
A spokeswoman for the British Museum said it was making the Rosetta Stone as accessible as possible by publishing a 3D scan online, working with Egyptian colleagues and organising a new exhibition on Egypt.
The planned exhibition will be a “once-in-a-lifetime opportunity for visitors to learn more about the Rosetta Stone’s significance and legacy”, she said.
But Dr Hawass is not backing down on his mission to put the Rosetta Stone in the unfinished Grand Egyptian Museum in Cairo — even if it takes more than a lifetime to make it happen.
“If I did not succeed, at least people after me will continue,” he said. “This is a case that you cannot stop.”