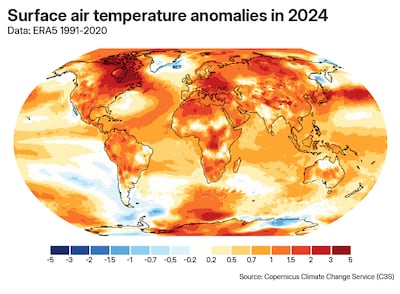
Earth’s temperature remained 1.5°C above the pre-industrial average in 2024, representing the first calendar-long breach of the milestone on record.
Copernicus, EU's climate change monitoring service, said the global temperature average of 15.10°C was 0.12°C above 2023's level, the previous warmest year. It was also 1.60°C higher than the temperature estimate for the pre-fossil fuel era, from 1850 to 1900.
Scientists said the figures suggested it was now “very likely” the world would fail to reach its 2060 global warming targets.
Akshay Deoras, a research scientist at the National Centre for Atmospheric Science and the Department of Meteorology at the University of Reading, told The National that the milestone showed humanity was “treating our planet like a credit card with no limit”.
“The annual global temperature crossing the 1.5°C mark for the first time in 2024 shows the bill is coming, which unfortunately could lead to a further increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events across the globe,” Mr Deoras said.
To breach the 2015 Paris Agreement, the average global temperature over a period of at least 20 years must exceed the temperature recorded during the pre-industrial period by at least 1.5°C, he added.
“Whilst we are yet to breach the Paris Agreement, several consecutive months since summer 2023 have been warmer by at least 1.5°C, showing how serious the problem of global warming is," he explained. "The more often 1.5°C threshold gets breached, the closer we would be to the breaching of the Paris Agreement.
“We're already seeing homes become uninsurable and disasters costing billions. This isn't about future generations any more – it's about us, today. We are on track to see new warming records getting broken, unless we immediately cut down the emission of greenhouse gases."
Another report released on Friday by the UN's World Meteorological Organisation, which synthesised data from six regional climate monitoring institutes, found that the years from 2014 to 2024 were the 10 warmest on record.
“Today’s assessment from the World Meteorological Organisation proves yet again global heating is a cold, hard fact,” UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres said.
The UN chief called on world governments to “act now” and submit updated national climate plans for 2025 as well as supporting those most affected by severe climate impacts.
But “individual years pushing past the 1.5-degree limit do not mean the long-term goal is shot. It means we need to fight even harder to get on track," he added.
WMO secretary general Celeste Saulo said it is “essential to recognise that every fraction of a degree of warming matters”.
She added: “Whether it is at a level below or above 1.5°C of warming, every additional increment of global warming increases the impacts on our lives, economies and our planet.”
During the first half of last year, which was the world's hottest on record, each month registered higher readings than the same month in any previous year. That led to a 13-month streak of record temperatures.
Global temperatures remained significantly above average in the second half of last year. The world set a record daily global average temperature of 17.16°C on July 22.
It was the warmest year for all continental regions, except Antarctica and Australasia, as well as for sizeable parts of the ocean, particularly the North Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.
Around Antarctica, sea ice reached record or near-record lows during a large part of the year, while in the Arctic, the sea ice extent was relatively close to its 1991 to 2020 average until July, but fell well below average in the following months. At its annual minimum in September, levels were fifth lowest in the satellite record.
Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, said he was “running out of metaphors” to explain the warming.
“The many record breaking events that we have seen over the course of the last 12 months are not statistical oddities, but rather a direct consequence of the generalised warming of our climate system,” he said. “The underlying physics is very clear. A warmer global climate produces more frequent and intense events, such as for example, heatwaves. A warmer atmosphere also holds more moisture, leading to heavier rainfall, where warmer seas amplify the potential for destructive storms."
The Paris Agreement’s long-term goal to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels was chosen to avoid the most severe effects of climate change, albeit with more common extreme heatwaves and drought compared with today. Under this scenario, the world is expected to exceed 1.5°C from 2030, before dropping below 1.5°C by 2060.
Samantha Burgess, strategic lead for climate at Copernicus, said on Thursday that 2024’s milestone meant it was “very likely” the world would miss the target.
“Given that we have had our first calendar year of 1.5ºC, there is an extremely high likelihood that we will overshoot the long-term average of 1.5ºC and the Paris Agreement limit," she said.
“However, my personal opinion is that this is an extraordinarily important policy that all countries around the world have committed to, so I don’t think it’s fair to say the Paris Agreement is dead. And I think if we do overshoot 1.5ºC, which has a high probability associated with it, the next target does not automatically deflect to 2ºC, but the next target becomes 1.51ºC. And the sooner we get to net-zero emissions, the sooner we will stabilise our climate and reduce the potential impacts of future extreme events.”
Worsening warming
According to the Carbon Brief, if warming exceeds 1.5°C beyond 2100 and peaks at 1.89°C, sea levels will rise by 20cm at more than 70 per cent of the Earth's coastlines.
If warming continues to rise, peaking at 2.69°C by 2100, the world would pass a catastrophic point of no return, with the loss of all ice sheets, sea level rises of several metres, extreme heatwaves occurring most years and the drying out of the Amazon rainforest.
Warming of 4°C would result in unprecedented heatwaves, severe drought and major flooding, creating millions of global climate refugees. Wide-scale adaptation to global sea rise would also be necessary.
Adla Massoud contributed to this report from the United Nations
ICC T20 Rankings
1. India - 270 ranking points
2. England - 265 points
3. Pakistan - 261 points
4. South Africa - 253 points
5. Australia - 251 points
6. New Zealand - 250 points
7. West Indies - 240 points
8. Bangladesh - 233 points
9. Sri Lanka - 230 points
10. Afghanistan - 226 points
Turning%20waste%20into%20fuel
%3Cp%3EAverage%20amount%20of%20biofuel%20produced%20at%20DIC%20factory%20every%20month%3A%20%3Cstrong%3EApproximately%20106%2C000%20litres%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EAmount%20of%20biofuel%20produced%20from%201%20litre%20of%20used%20cooking%20oil%3A%20%3Cstrong%3E920ml%20(92%25)%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3ETime%20required%20for%20one%20full%20cycle%20of%20production%20from%20used%20cooking%20oil%20to%20biofuel%3A%20%3Cstrong%3EOne%20day%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EEnergy%20requirements%20for%20one%20cycle%20of%20production%20from%201%2C000%20litres%20of%20used%20cooking%20oil%3A%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3E%E2%96%AA%20Electricity%20-%201.1904%20units%3Cbr%3E%E2%96%AA%20Water-%2031%20litres%3Cbr%3E%E2%96%AA%20Diesel%20%E2%80%93%2026.275%20litres%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Company profile: buybackbazaar.com
Name: buybackbazaar.com
Started: January 2018
Founder(s): Pishu Ganglani and Ricky Husaini
Based: Dubai
Sector: FinTech, micro finance
Initial investment: $1 million
The%20National%20selections
%3Cp%3E%3Cspan%20style%3D%22font-size%3A%2014px%3B%22%3E6pm%3A%20Go%20Soldier%20Go%3Cbr%3E6.35pm%3A%20Man%20Of%20Promise%3Cbr%3E7.10pm%3A%20Withering%3Cbr%3E7.45pm%3A%20Mawj%3Cbr%3E8.20pm%3A%20Falling%20Shadow%3Cbr%3E8.55pm%3A%20Law%20Of%20Peace%3Cbr%3E9.30pm%3A%20Naval%20Power%3Cbr%3E10.05pm%3A%20The%20Attorney%3C%2Fspan%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Red flags
- Promises of high, fixed or 'guaranteed' returns.
- Unregulated structured products or complex investments often used to bypass traditional safeguards.
- Lack of clear information, vague language, no access to audited financials.
- Overseas companies targeting investors in other jurisdictions - this can make legal recovery difficult.
- Hard-selling tactics - creating urgency, offering 'exclusive' deals.
Courtesy: Carol Glynn, founder of Conscious Finance Coaching
Profile
Name: Carzaty
Founders: Marwan Chaar and Hassan Jaffar
Launched: 2017
Employees: 22
Based: Dubai and Muscat
Sector: Automobile retail
Funding to date: $5.5 million
UAE currency: the story behind the money in your pockets
Key facilities
- Olympic-size swimming pool with a split bulkhead for multi-use configurations, including water polo and 50m/25m training lanes
- Premier League-standard football pitch
- 400m Olympic running track
- NBA-spec basketball court with auditorium
- 600-seat auditorium
- Spaces for historical and cultural exploration
- An elevated football field that doubles as a helipad
- Specialist robotics and science laboratories
- AR and VR-enabled learning centres
- Disruption Lab and Research Centre for developing entrepreneurial skills
How to help
Send “thenational” to the following numbers or call the hotline on: 0502955999
2289 – Dh10
2252 – Dh 50
6025 – Dh20
6027 – Dh 100
6026 – Dh 200
German intelligence warnings
- 2002: "Hezbollah supporters feared becoming a target of security services because of the effects of [9/11] ... discussions on Hezbollah policy moved from mosques into smaller circles in private homes." Supporters in Germany: 800
- 2013: "Financial and logistical support from Germany for Hezbollah in Lebanon supports the armed struggle against Israel ... Hezbollah supporters in Germany hold back from actions that would gain publicity." Supporters in Germany: 950
- 2023: "It must be reckoned with that Hezbollah will continue to plan terrorist actions outside the Middle East against Israel or Israeli interests." Supporters in Germany: 1,250
Source: Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution
Our legal advisor
Rasmi Ragy is a senior counsel at Charles Russell Speechlys, a law firm headquartered in London with offices in Europe, the Middle East and Hong Kong.
Experience: Prosecutor in Egypt with more than 40 years experience across the GCC.
Education: Ain Shams University, Egypt, in 1978.
Switching%20sides
%3Cp%3EMahika%20Gaur%20is%20the%20latest%20Dubai-raised%20athlete%20to%20attain%20top%20honours%20with%20another%20country.%0D%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EVelimir%20Stjepanovic%20(Serbia%2C%20swimming)%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3EBorn%20in%20Abu%20Dhabi%20and%20raised%20in%20Dubai%2C%20he%20finished%20sixth%20in%20the%20final%20of%20the%202012%20Olympic%20Games%20in%20London%20in%20the%20200m%20butterfly%20final.%20%0D%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EJonny%20Macdonald%20(Scotland%2C%20rugby%20union)%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3EBrought%20up%20in%20Abu%20Dhabi%20and%20represented%20the%20region%20in%20international%20rugby.%20When%20the%20Arabian%20Gulf%20team%20was%20broken%20up%20into%20its%20constituent%20nations%2C%20he%20opted%20to%20play%20for%20Scotland%20instead%2C%20and%20went%20to%20the%20Hong%20Kong%20Sevens.%20%0D%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ESophie%20Shams%20(England%2C%20rugby%20union)%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3EThe%20daughter%20of%20an%20English%20mother%20and%20Emirati%20father%2C%20Shams%20excelled%20at%20rugby%20in%20Dubai%2C%20then%20after%20attending%20university%20in%20the%20UK%20played%20for%20England%20at%20sevens.%20%0D%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Labour dispute
The insured employee may still file an ILOE claim even if a labour dispute is ongoing post termination, but the insurer may suspend or reject payment, until the courts resolve the dispute, especially if the reason for termination is contested. The outcome of the labour court proceedings can directly affect eligibility.
- Abdullah Ishnaneh, Partner, BSA Law
KILLING OF QASSEM SULEIMANI
%3Cp%3EThe%20Department%20of%20Culture%20and%20Tourism%20-%20Abu%20Dhabi%E2%80%99s%20Arabic%20Language%20Centre%20will%20mark%20International%20Women%E2%80%99s%20Day%20at%20the%20Bologna%20Children's%20Book%20Fair%20with%20the%20Abu%20Dhabi%20Translation%20Conference.%20Prolific%20Emirati%20author%20Noora%20Al%20Shammari%2C%20who%20has%20written%20eight%20books%20that%20%20feature%20in%20the%20Ministry%20of%20Education's%20curriculum%2C%20will%20appear%20in%20a%20session%20on%20Wednesday%20to%20discuss%20the%20challenges%20women%20face%20in%20getting%20their%20works%20translated.%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
The specs
Engine: 2.0-litre 4-cyl turbo
Power: 247hp at 6,500rpm
Torque: 370Nm from 1,500-3,500rpm
Transmission: 10-speed auto
Fuel consumption: 7.8L/100km
Price: from Dh94,900
On sale: now
WITHIN%20SAND
%3Cp%3EDirector%3A%20Moe%20Alatawi%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EStarring%3A%20Ra%E2%80%99ed%20Alshammari%2C%20Adwa%20Fahd%2C%20Muhand%20Alsaleh%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3ERating%3A%203%2F5%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
2019 ASIA CUP POTS
Pot 1
UAE, Iran, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Saudi Arabia
Pot 2
China, Syria, Uzbekistan, Iraq, Qatar, Thailand
Pot 3
Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Palestine, Oman, India, Vietnam
Pot 4
North Korea, Philippines, Bahrain, Jordan, Yemen, Turkmenistan
The%20specs%3A%202024%20Mercedes%20E200
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EEngine%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E2.0-litre%20four-cyl%20turbo%20%2B%20mild%20hybrid%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPower%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E204hp%20at%205%2C800rpm%20%2B23hp%20hybrid%20boost%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETorque%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E320Nm%20at%201%2C800rpm%20%2B205Nm%20hybrid%20boost%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETransmission%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E9-speed%20auto%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EFuel%20consumption%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E7.3L%2F100km%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EOn%20sale%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3ENovember%2FDecember%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPrice%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EFrom%20Dh205%2C000%20(estimate)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
More from Rashmee Roshan Lall
Fifa%20World%20Cup%20Qatar%202022%20
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EFirst%20match%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3ENovember%2020%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EFinal%2016%20round%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EDecember%203%20to%206%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EQuarter-finals%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EDecember%209%20and%2010%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ESemi-finals%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EDecember%2013%20and%2014%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EFinal%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EDecember%2018%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Calls
Directed by: Fede Alvarez
Starring: Pedro Pascal, Karen Gillian, Aaron Taylor-Johnson
4/5
Our legal consultant
Name: Dr Hassan Mohsen Elhais
Position: legal consultant with Al Rowaad Advocates and Legal Consultants.
On the menu
First course
▶ Emirati sea bass tartare Yuzu and labneh mayo, avocado, green herbs, fermented tomato water
▶ The Tale of the Oyster Oyster tartare, Bahraini gum berry pickle
Second course
▶ Local mackerel Sourdough crouton, baharat oil, red radish, zaatar mayo
▶ One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest Quail, smoked freekeh, cinnamon cocoa
Third course
▶ Bahraini bouillabaisse Venus clams, local prawns, fishfarm seabream, farro
▶ Lamb 2 ways Braised lamb, crispy lamb chop, bulgur, physalis
Dessert
▶ Lumi Black lemon ice cream, pistachio, pomegranate
▶ Black chocolate bar Dark chocolate, dates, caramel, camel milk ice cream
MORE ON CORONAVIRUS & THE ECONOMY