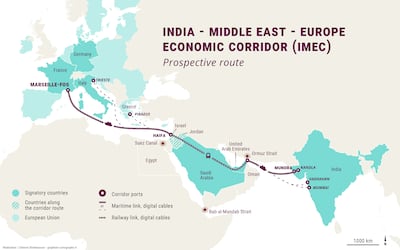
When I took part in the Delphi Economic Forum in Greece this month, discussions centred on the prerequisites for transformative corridor projects in the Middle East, such as the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, the Belt and Road Initiative and the Iraq Development Road. Security, political stability and an end to wars emerged as essential conditions.
However, critical questions were raised at the forum. Do these major projects clash with each other, or can they be complementary? Can trust-building among political actors bridge gaps and strengthen incentives for co-operation? And does US President Donald Trump have enough commitment to support, follow up and accelerate the launch of Imec?
Mohammed Baharoon, director general of the Dubai Policy Research Centre, and I represented the UAE in a session on Mediterranean-Gulf connectivity and the added value of corridor projects in deepening this connectivity. Our engagement highlighted how current geopolitical challenges have reshaped the momentum and feasibility of such initiatives, including Imec.
In general, the tragic war in Gaza has stalled the project’s momentum, as envisioned at its launch during the G20 Summit in New Delhi in September 2023. This war and the significant regional shifts since October 7 that year highlight the need for a reassessment to broaden participation in Imec and other such transformative mega projects. Improved Syrian-Iraqi relations could represent a significant step towards better integration of the two countries – as well as Lebanon, and perhaps even Gaza – into these corridors.
Imec gives economic diplomacy a more influential role in shaping the prospects of international relations, directing priorities and resources towards greater co-operation and economic interests rather than conflict. However, geopolitics is far from absent. The Gaza war and the resulting escalation between Israel and Iran, for example, were clear evidence of this. Instability also derails progress: the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, for instance, faltered largely due to political and social instability in Pakistan.
The UAE advocates a more pragmatic and sustainable approach that considers projects and initiatives such as BRI, Imec and the Iraq Development Road (which includes the UAE, Qatar, Iraq and Turkey) as complementary rather than confrontational
Among the challenges this project faces is the question of who will fund the tens of billions of dollars needed to improve existing infrastructure and address gaps remains unanswered. Imec requires more than 2,000 kilometres of railway, and large parts of it still need to be built in the Middle East’s rough terrain. For example, the shipping route from Haifa in Israel to Greece passes through waters disputed with Turkey, which is not part of the project.
Ankara’s objections to the project could become more vocal following the shift in Syria with the fall of Bashar Al Assad’s government last December and the subsequent rise in Turkish influence in the country. The exclusion of Egypt, Iraq and Oman from Imec could also pose some challenges to the project.
Therefore, the UAE advocates a more pragmatic and sustainable approach that considers projects and initiatives such as BRI, Imec and the Iraq Development Road (which includes the UAE, Qatar, Iraq and Turkey) as complementary rather than confrontational. This inclusive view offers the most practical and sustainable path forward.
While Turkey is apprehensive about Imec, which does not pass through its territory, Ankara’s involvement in the Iraq Development Road will determine whether this project competes with or complements Imec. Turkey’s role will also determine the extent to which the Iraq Development Road supports China’s BRI.
Chinese experts have so far expressed scepticism towards the infrastructure proposals associated with Imec, criticising what they see as a familiar US pattern of overpromising and underdelivering.
While Imec struggles to compete with BRI – a decade-old framework involving about 150 countries – it aligns with US efforts to empower a select group of “technically and financially capable” states. For China, Imec presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Just as the US has often downplayed BRI’s significance, Beijing may regard Imec with initial scepticism. However, the best-case scenario for all parties would be one of co-operation and constructive competition, rather than rivalry or confrontation.
It is evident that the UAE continues to pursue a multilateral foreign policy.
During his meeting with Chinese Premier Li Qiang in Abu Dhabi last September, President Sheikh Mohamed reaffirmed his country’s commitment as a strategic partner in BRI. He also emphasised that UAE-China relations represent a model of international co-operation rooted in diplomacy and dialogue.
China remains the UAE’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade reaching $102 billion last year – marking a 7 per cent increase from 2023. In a first-of-its-kind development that will further deepen economic and tourism ties, China Eastern Airlines announced the launch of direct flights between Shanghai and Abu Dhabi, scheduled to begin today.
This move underscores Abu Dhabi’s strategic importance within the BRI framework. The emirate offers a supportive economic environment – bolstered by its advantageous geographic location, investor-friendly free zone policies and leadership in the energy and financial services sectors – making it an ideal hub for the global expansion of Chinese enterprises.
As economic ties deepen, with bilateral trade between the UAE and China projected to reach $200 billion by 2030, Abu Dhabi is steadily reinforcing its role as a gateway for Chinese investment into the Middle East and beyond. The emirate now hosts a significant number of Chinese companies operating in key sectors such as high tech, financial services, energy and industry.
Yet while China continues to deepen its BRI footprint, questions remain about the future of US-backed initiatives.
Mr Trump’s protectionist orientation has cast doubt on the depth of US commitment to Imec, which has been described as a potential catalyst for realising the long-envisioned Eurasian connectivity. While Mr Trump characterised Imec as “one of the greatest trade routes in history” during his meeting with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in February, expectations must be tempered by the need for realistic, adaptable approaches.
In the end, the success of Imec – and similar large-scale initiatives – depends on the ability of stakeholders to embrace a co-operative, win-win approach. Prioritising complementarity rather than rivalry is key to realising the full potential of regional connectivity.
Step by step
2070km to run
38 days
273,600 calories consumed
28kg of fruit
40kg of vegetables
45 pairs of running shoes
1 yoga matt
1 oxygen chamber
Engine: 5.6-litre V8
Transmission: seven-speed automatic
Power: 400hp
Torque: 560Nm
Price: Dh234,000 - Dh329,000
On sale: now
Profile of Tarabut Gateway
Founder: Abdulla Almoayed
Based: UAE
Founded: 2017
Number of employees: 35
Sector: FinTech
Raised: $13 million
Backers: Berlin-based venture capital company Target Global, Kingsway, CE Ventures, Entrée Capital, Zamil Investment Group, Global Ventures, Almoayed Technologies and Mad’a Investment.
The%20specs%20
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EEngine%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E2.0-litre%204cyl%20turbo%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPower%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E261hp%20at%205%2C500rpm%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETorque%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E400Nm%20at%201%2C750-4%2C000rpm%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETransmission%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E7-speed%20dual-clutch%20auto%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EFuel%20consumption%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E10.5L%2F100km%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EOn%20sale%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3ENow%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPrice%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EFrom%20Dh129%2C999%20(VX%20Luxury)%3B%20from%20Dh149%2C999%20(VX%20Black%20Gold)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Avatar%3A%20The%20Way%20of%20Water
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EDirector%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EJames%20Cameron%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EStars%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3ESam%20Worthington%2C%20Zoe%20Saldana%2C%20Sigourney%20Weaver%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ERating%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E3.5%2F5%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
More on animal trafficking
Libya's Gold
UN Panel of Experts found regime secretly sold a fifth of the country's gold reserves.
The panel’s 2017 report followed a trail to West Africa where large sums of cash and gold were hidden by Abdullah Al Senussi, Qaddafi’s former intelligence chief, in 2011.
Cases filled with cash that was said to amount to $560m in 100 dollar notes, that was kept by a group of Libyans in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.
A second stash was said to have been held in Accra, Ghana, inside boxes at the local offices of an international human rights organisation based in France.
Five%20calorie-packed%20Ramadan%20drinks
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ERooh%20Afza%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3E100ml%20contains%20414%20calories%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETang%20orange%20drink%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3E100ml%20serving%20contains%20300%20calories%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ECarob%20beverage%20mix%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3E100ml%20serving%20contains%20about%20300%20calories%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EQamar%20Al%20Din%20apricot%20drink%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3E100ml%20saving%20contains%2061%20calories%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EVimto%20fruit%20squash%3C%2Fstrong%3E%0D%3Cbr%3E100ml%20serving%20contains%2030%20calories%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
THE BIO
Ms Davison came to Dubai from Kerala after her marriage in 1996 when she was 21-years-old
Since 2001, Ms Davison has worked at many affordable schools such as Our Own English High School in Sharjah, and The Apple International School and Amled School in Dubai
Favourite Book: The Alchemist
Favourite quote: Failing to prepare is preparing to fail
Favourite place to Travel to: Vienna
Favourite cuisine: Italian food
Favourite Movie : Scent of a Woman
2.0
Director: S Shankar
Producer: Lyca Productions; presented by Dharma Films
Cast: Rajnikanth, Akshay Kumar, Amy Jackson, Sudhanshu Pandey
Rating: 3.5/5 stars
A little about CVRL
Founded in 1985 by Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid, Vice President and Ruler of Dubai, the Central Veterinary Research Laboratory (CVRL) is a government diagnostic centre that provides testing and research facilities to the UAE and neighbouring countries.
One of its main goals is to provide permanent treatment solutions for veterinary related diseases.
The taxidermy centre was established 12 years ago and is headed by Dr Ulrich Wernery.
Avatar: Fire and Ash
Director: James Cameron
Starring: Sam Worthington, Sigourney Weaver, Zoe Saldana
Rating: 4.5/5
A list of the animal rescue organisations in the UAE
MATCH INFO
What: India v Afghanistan, first Test
When: Starts Thursday
Where: M Chinnaswamy Stadium, Bengalaru
Indoor cricket in a nutshell
Indoor cricket in a nutshell
Indoor Cricket World Cup - Sept 16-20, Insportz, Dubai
16 Indoor cricket matches are 16 overs per side
8 There are eight players per team
9 There have been nine Indoor Cricket World Cups for men. Australia have won every one.
5 Five runs are deducted from the score when a wickets falls
4 Batsmen bat in pairs, facing four overs per partnership
Scoring In indoor cricket, runs are scored by way of both physical and bonus runs. Physical runs are scored by both batsmen completing a run from one crease to the other. Bonus runs are scored when the ball hits a net in different zones, but only when at least one physical run is score.
Zones
A Front net, behind the striker and wicketkeeper: 0 runs
B Side nets, between the striker and halfway down the pitch: 1 run
C Side nets between halfway and the bowlers end: 2 runs
D Back net: 4 runs on the bounce, 6 runs on the full
EA Sports FC 25
Developer: EA Vancouver, EA Romania
Publisher: EA Sports
Consoles: Nintendo Switch, PlayStation 4&5, Xbox One and Xbox Series X/S
Rating: 3.5/5
SPEC%20SHEET%3A%20SAMSUNG%20GALAXY%20Z%20FOLD%204
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EMain%20display%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%207.6%22%20QXGA%2B%20Dynamic%20Amoled%202X%2C%202176%20x%201812%2C%2021.6%3A18%2C%20374ppi%2C%20HDR10%2B%2C%20up%20to%20120Hz%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ECover%20display%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%206.2%22%20HD%2B%20Dynamic%20Amoled%202X%2C%202316%20x%20904%2C%2023.1%3A9%2C%20402ppi%2C%20up%20to%20120Hz%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EProcessor%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Qualcomm%20Snapdragon%208%2B%20Gen%201%2C%204nm%2C%20octa-core%3B%20Adreno%20730%20GPU%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EMemory%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%2012GB%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ECapacity%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%C2%A0256%2F512GB%20%2F%201TB%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EPlatform%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Android%2012%2C%20One%20UI%204.1.1%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EMain%20camera%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Triple%2012MP%20ultra-wide%20(f%2F2.2)%20%2B%2050MP%20wide%20(f%2F1.8)%20%2B%2010MP%20telephoto%20(f%2F2.4)%2C%20dual%20OIS%2C%203x%20optical%20zoom%2C%2030x%20Space%20Zoom%2C%20portrait%2C%20super%20slo-mo%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EVideo%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%208K%4024fps%2C%204K%4030%2F60fps%2C%20full-HD%4030%2F60fps%2C%20HD%4030fps%3B%20slo-mo%4060%2F240%2F960fps%3B%20HDR10%2B%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ECover%20camera%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%2010MP%20(f%2F2.2)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EInner%20front%20camera%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Under-display%204MP%20(f%2F1.8)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EBattery%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%204400mAh%2C%2025W%20fast%20charging%2C%2015W%20wireless%20charging%2C%20reverse%20wireless%20charging%2C%20'all-day'%20life%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EConnectivity%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%205G%3B%20Wi-Fi%2C%20Bluetooth%205.2%2C%20NFC%20(Samsung%20Pay)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EI%2FO%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20USB-C%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3ECards%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Nano-SIM%20%2B%20eSIM%3B%202%20nano-SIMs%20%2B%20eSIM%3B%202%20nano-SIMs%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EColours%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Graygreen%2C%20phantom%20black%2C%20beige%2C%20burgundy%20(online%20exclusive)%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EIn%20the%20box%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Fold%204%2C%20USB-C-to-USB-C%20cable%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EPrice%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Dh6%2C799%20%2F%20Dh7%2C249%20%2F%20Dh8%2C149%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
25%20Days%20to%20Aden
%3Cp%3EAuthor%3A%20Michael%20Knights%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EPages%3A%20256%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EAvailable%3A%20January%2026%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Turning%20waste%20into%20fuel
%3Cp%3EAverage%20amount%20of%20biofuel%20produced%20at%20DIC%20factory%20every%20month%3A%20%3Cstrong%3EApproximately%20106%2C000%20litres%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EAmount%20of%20biofuel%20produced%20from%201%20litre%20of%20used%20cooking%20oil%3A%20%3Cstrong%3E920ml%20(92%25)%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3ETime%20required%20for%20one%20full%20cycle%20of%20production%20from%20used%20cooking%20oil%20to%20biofuel%3A%20%3Cstrong%3EOne%20day%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A%3Cp%3EEnergy%20requirements%20for%20one%20cycle%20of%20production%20from%201%2C000%20litres%20of%20used%20cooking%20oil%3A%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3E%E2%96%AA%20Electricity%20-%201.1904%20units%3Cbr%3E%E2%96%AA%20Water-%2031%20litres%3Cbr%3E%E2%96%AA%20Diesel%20%E2%80%93%2026.275%20litres%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
The%C2%A0specs%20
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EEngine%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Dual%20synchronous%20electric%20motors%20%20%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPower%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E646hp%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETorque%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3E830Nm%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETransmission%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3ETwo-speed%20auto%20(rear%20axle)%3B%20single-speed%20auto%20(front)%20%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPrice%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3EFrom%20Dh552%2C311%3B%20Dh660%2C408%20(as%20tested)%0D%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EOn%20sale%3A%20%3C%2Fstrong%3Enow%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
List of alleged parties
May 12, 2020: PM and his wife Carrie attend 'work meeting' with at least 17 staff
May 20, 2020: They attend 'bring your own booze party'
Nov 27, 2020: PM gives speech at leaving party for his staff
Dec 10, 2020: Staff party held by then-education secretary Gavin Williamson
Dec 13, 2020: PM and his wife throw a party
Dec 14, 2020: London mayoral candidate Shaun Bailey holds staff event at Conservative Party headquarters
Dec 15, 2020: PM takes part in a staff quiz
Dec 18, 2020: Downing Street Christmas party
Sholto Byrnes on Myanmar politics
From Zero
Artist: Linkin Park
Label: Warner Records
Number of tracks: 11
Rating: 4/5
Emergency
Director: Kangana Ranaut
Stars: Kangana Ranaut, Anupam Kher, Shreyas Talpade, Milind Soman, Mahima Chaudhry
Rating: 2/5
Star%20Wars%3A%20Ahsoka%20
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EDirector%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Various%20%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EStarring%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Rosario%20Dawson%2C%20Natasha%20Liu%20Bordizzo%2C%20Lars%20Mikkelsen%20%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ERating%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%204%2F5%0D%3Cbr%3E%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Sly%20Cooper%20and%20the%20Thievius%20Raccoonus
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EDeveloper%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Sucker%20Punch%20Productions%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPublisher%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Sony%20Computer%20Entertainment%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EConsole%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20PlayStation%202%20to%205%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ERating%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%205%2F5%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
SPECS
%3Cp%3E%3Cstrong%3EEngine%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%201.5-litre%204-cylinder%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPower%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20101hp%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETorque%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20135Nm%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3ETransmission%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3A%20Six-speed%20auto%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EPrice%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20From%20Dh79%2C900%3Cbr%3E%3Cstrong%3EOn%20sale%3A%3C%2Fstrong%3E%20Now%3C%2Fp%3E%0A
Company info
Company name: Entrupy
Co-founders: Vidyuth Srinivasan, co-founder/chief executive, Ashlesh Sharma, co-founder/chief technology officer, Lakshmi Subramanian, co-founder/chief scientist
Based: New York, New York
Sector/About: Entrupy is a hardware-enabled SaaS company whose mission is to protect businesses, borders and consumers from transactions involving counterfeit goods.
Initial investment/Investors: Entrupy secured a $2.6m Series A funding round in 2017. The round was led by Tokyo-based Digital Garage and Daiwa Securities Group's jointly established venture arm, DG Lab Fund I Investment Limited Partnership, along with Zach Coelius.
Total customers: Entrupy’s customers include hundreds of secondary resellers, marketplaces and other retail organisations around the world. They are also testing with shipping companies as well as customs agencies to stop fake items from reaching the market in the first place.
Our legal consultant
Name: Hassan Mohsen Elhais
Position: legal consultant with Al Rowaad Advocates and Legal Consultants.
Timeline
2012-2015
The company offers payments/bribes to win key contracts in the Middle East
May 2017
The UK SFO officially opens investigation into Petrofac’s use of agents, corruption, and potential bribery to secure contracts
September 2021
Petrofac pleads guilty to seven counts of failing to prevent bribery under the UK Bribery Act
October 2021
Court fines Petrofac £77 million for bribery. Former executive receives a two-year suspended sentence
December 2024
Petrofac enters into comprehensive restructuring to strengthen the financial position of the group
May 2025
The High Court of England and Wales approves the company’s restructuring plan
July 2025
The Court of Appeal issues a judgment challenging parts of the restructuring plan
August 2025
Petrofac issues a business update to execute the restructuring and confirms it will appeal the Court of Appeal decision
October 2025
Petrofac loses a major TenneT offshore wind contract worth €13 billion. Holding company files for administration in the UK. Petrofac delisted from the London Stock Exchange
November 2025
180 Petrofac employees laid off in the UAE
Explainer: Tanween Design Programme
Non-profit arts studio Tashkeel launched this annual initiative with the intention of supporting budding designers in the UAE. This year, three talents were chosen from hundreds of applicants to be a part of the sixth creative development programme. These are architect Abdulla Al Mulla, interior designer Lana El Samman and graphic designer Yara Habib.
The trio have been guided by experts from the industry over the course of nine months, as they developed their own products that merge their unique styles with traditional elements of Emirati design. This includes laboratory sessions, experimental and collaborative practice, investigation of new business models and evaluation.
It is led by British contemporary design project specialist Helen Voce and mentor Kevin Badni, and offers participants access to experts from across the world, including the likes of UK designer Gareth Neal and multidisciplinary designer and entrepreneur, Sheikh Salem Al Qassimi.
The final pieces are being revealed in a worldwide limited-edition release on the first day of Downtown Designs at Dubai Design Week 2019. Tashkeel will be at stand E31 at the exhibition.
Lisa Ball-Lechgar, deputy director of Tashkeel, said: “The diversity and calibre of the applicants this year … is reflective of the dynamic change that the UAE art and design industry is witnessing, with young creators resolute in making their bold design ideas a reality.”
Dubai World Cup Carnival card
6.30pm: UAE 1000 Guineas Trial Conditions (TB) US$100,000 (Dirt) 1,400m
7.05pm: Handicap (TB) $135,000 (Turf) 1,000m
7.40pm: Handicap (TB) $175,000 (D) 1,900m
8.15pm: Meydan Challenge Listed Handicap (TB) $175,000 (T) 1,400m
8.50pm: Dubai Stakes Group 3 (TB) $200,000 (D) 1,200m
9.25pm: Dubai Racing Club Classic Listed Handicap (TB) $175,000 (T) 2,410m
The National selections
6.30pm: Final Song
7.05pm: Pocket Dynamo
7.40pm: Dubai Icon
8.15pm: Dubai Legacy
8.50pm: Drafted
9.25pm: Lucius Tiberius
The specs
Engine: 2.0-litre turbo 4-cyl
Transmission: eight-speed auto
Power: 190bhp
Torque: 300Nm
Price: Dh169,900
On sale: now
Ten tax points to be aware of in 2026
1. Domestic VAT refund amendments: request your refund within five years
If a business does not apply for the refund on time, they lose their credit.
2. E-invoicing in the UAE
Businesses should continue preparing for the implementation of e-invoicing in the UAE, with 2026 a preparation and transition period ahead of phased mandatory adoption.
3. More tax audits
Tax authorities are increasingly using data already available across multiple filings to identify audit risks.
4. More beneficial VAT and excise tax penalty regime
Tax disputes are expected to become more frequent and more structured, with clearer administrative objection and appeal processes. The UAE has adopted a new penalty regime for VAT and excise disputes, which now mirrors the penalty regime for corporate tax.
5. Greater emphasis on statutory audit
There is a greater need for the accuracy of financial statements. The International Financial Reporting Standards standards need to be strictly adhered to and, as a result, the quality of the audits will need to increase.
6. Further transfer pricing enforcement
Transfer pricing enforcement, which refers to the practice of establishing prices for internal transactions between related entities, is expected to broaden in scope. The UAE will shortly open the possibility to negotiate advance pricing agreements, or essentially rulings for transfer pricing purposes.
7. Limited time periods for audits
Recent amendments also introduce a default five-year limitation period for tax audits and assessments, subject to specific statutory exceptions. While the standard audit and assessment period is five years, this may be extended to up to 15 years in cases involving fraud or tax evasion.
8. Pillar 2 implementation
Many multinational groups will begin to feel the practical effect of the Domestic Minimum Top-Up Tax (DMTT), the UAE's implementation of the OECD’s global minimum tax under Pillar 2. While the rules apply for financial years starting on or after January 1, 2025, it is 2026 that marks the transition to an operational phase.
9. Reduced compliance obligations for imported goods and services
Businesses that apply the reverse-charge mechanism for VAT purposes in the UAE may benefit from reduced compliance obligations.
10. Substance and CbC reporting focus
Tax authorities are expected to continue strengthening the enforcement of economic substance and Country-by-Country (CbC) reporting frameworks. In the UAE, these regimes are increasingly being used as risk-assessment tools, providing tax authorities with a comprehensive view of multinational groups’ global footprints and enabling them to assess whether profits are aligned with real economic activity.
Contributed by Thomas Vanhee and Hend Rashwan, Aurifer
Cricket World Cup League Two
Oman, UAE, Namibia
Al Amerat, Muscat
Results
Oman beat UAE by five wickets
UAE beat Namibia by eight runs
Fixtures
Wednesday January 8 –Oman v Namibia
Thursday January 9 – Oman v UAE
Saturday January 11 – UAE v Namibia
Sunday January 12 – Oman v Namibia
Tamkeen's offering
- Option 1: 70% in year 1, 50% in year 2, 30% in year 3
- Option 2: 50% across three years
- Option 3: 30% across five years
Section 375
Cast: Akshaye Khanna, Richa Chadha, Meera Chopra & Rahul Bhat
Director: Ajay Bahl
Producers: Kumar Mangat Pathak, Abhishek Pathak & SCIPL
Rating: 3.5/5
Tips for used car buyers
- Choose cars with GCC specifications
- Get a service history for cars less than five years old
- Don’t go cheap on the inspection
- Check for oil leaks
- Do a Google search on the standard problems for your car model
- Do your due diligence. Get a transfer of ownership done at an official RTA centre
- Check the vehicle’s condition. You don’t want to buy a car that’s a good deal but ends up costing you Dh10,000 in repairs every month
- Validate warranty and service contracts with the relevant agency and and make sure they are valid when ownership is transferred
- If you are planning to sell the car soon, buy one with a good resale value. The two most popular cars in the UAE are black or white in colour and other colours are harder to sell
Tarek Kabrit, chief executive of Seez, and Imad Hammad, chief executive and co-founder of CarSwitch.com